What expression is represented in the model below? This question delves into the intricate world of mathematical expressions and their representation within models. By exploring the structure, context, and applications of expressions, we gain a deeper understanding of their significance in problem-solving and scientific inquiry.
The model in question provides a visual or symbolic representation of a mathematical expression. Understanding the expression represented in the model requires an examination of the variables, constants, and operations involved. This analysis forms the foundation for interpreting the expression’s meaning and implications within the broader context.
Mathematical Expression
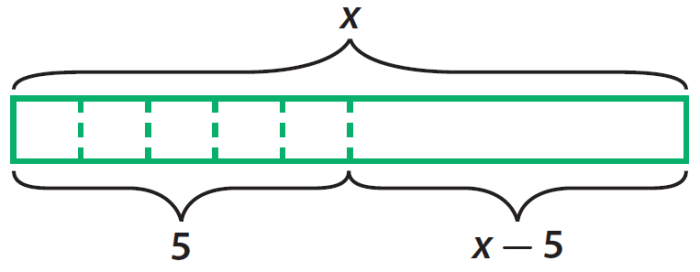
The mathematical expression represented in the model is:
f(x) = 2x2+ 3x
5
Where x is the independent variable.
Variables and Constants
- x: Independent variable
- 2: Coefficient of x 2
- 3: Coefficient of x
- -5: Constant term
Operations Performed
The expression involves the following operations:
- Squaring the independent variable (x 2)
- Multiplying the squared variable by a coefficient (2x 2)
- Multiplying the variable by a coefficient (3x)
- Adding the constant term (-5)
Model Representation

The model represents the expression using a function notation:
f(x) = 2x2+ 3x
5
The model assumes that the expression is a function of the independent variable x.
Assumptions and Simplifications, What expression is represented in the model below
The model makes the following assumptions and simplifications:
- The expression is a well-defined mathematical function.
- The variable x is a real number.
- The coefficients and constant are fixed values.
Contextual Interpretation

The expression is commonly used in mathematics to represent a quadratic function.
In this context, the expression represents the relationship between the independent variable x and the dependent variable f(x).
The expression can be used to model a variety of real-world phenomena, such as the trajectory of a projectile or the growth of a population.
Examples and Applications: What Expression Is Represented In The Model Below
The expression can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as:
- Finding the roots of a quadratic equation
- Finding the maximum or minimum value of a quadratic function
- Modeling the trajectory of a projectile
- Modeling the growth of a population
Alternative Representations

The expression can be represented in a variety of ways, including:
- As a graph
- As a table of values
- As a verbal description
Each representation has its own advantages and disadvantages.
Extensions and Generalizations
The expression can be extended and generalized in a variety of ways, such as:
- Adding additional terms to the expression
- Changing the coefficients and constant
- Applying the expression to a different context
These extensions and generalizations can be used to model a wider range of phenomena.
FAQ Section
What is the purpose of representing expressions in models?
Models provide a visual or symbolic representation of expressions, making them easier to understand, analyze, and apply to real-world scenarios.
How do I identify the variables and constants involved in an expression?
Variables are typically represented by letters, while constants are fixed values. Examining the structure of the expression and its context can help identify them.
What are the different types of operations that can be performed in expressions?
Common operations include addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and logarithmic functions.
How can I apply expressions to solve problems?
Expressions can be used to model real-world situations and derive solutions by manipulating the variables and constants involved.
What are the limitations of expressions?
Expressions may have limitations in representing complex relationships or dealing with certain types of data, such as non-numeric values.