Lasting improvement for a person with anorexia nervosa depends on a complex interplay of factors, including psychological, social, and treatment-related elements. This article delves into the multifaceted nature of recovery, exploring the essential components that contribute to successful outcomes.
Anorexia nervosa, an eating disorder characterized by severe food restriction and an intense fear of gaining weight, poses significant challenges to individuals and their loved ones. Understanding the underlying mechanisms that drive this condition is crucial for developing effective interventions and promoting lasting recovery.
Understanding Anorexia Nervosa

Anorexia nervosa is an eating disorder characterized by an intense fear of gaining weight, an unhealthy desire to be thin, and a disturbance in the way one perceives their body.
Individuals with anorexia nervosa restrict their food intake, engage in excessive exercise, and may resort to purging behaviors (such as vomiting or using laxatives) to lose weight. This can lead to severe malnutrition, electrolyte imbalances, and other health complications.
Psychological Effects
- Distorted body image
- Low self-esteem
- Anxiety and depression
- Obsessive-compulsive tendencies
Physiological Effects
- Weight loss
- Malnutrition
- Electrolyte imbalances
- Osteoporosis
- Cardiovascular problems
- Improved body image
- Increased self-esteem
- Reduced anxiety and depression
- Improved coping mechanisms
- Weight restoration
- Cognitive and behavioral changes
- Emotional healing
- Stress
- Negative body image
- Unresolved emotional issues
- Developing a relapse prevention plan
- Maintaining a healthy weight
- Engaging in regular therapy
- Seeking support from family and friends
- Severity of the disorder
- Age of onset
- Quality of treatment
- Level of support
Factors Contributing to Lasting Improvement
Psychological Factors
Family and Social Support
Family and social support are crucial for recovery. A supportive environment can provide encouragement, accountability, and a sense of belonging.
Addressing Underlying Emotional Issues
Anorexia nervosa is often a manifestation of underlying emotional issues, such as anxiety, depression, or trauma. Addressing these issues is essential for long-term recovery.
Treatment Approaches

Cognitive-Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
CBT helps individuals with anorexia nervosa challenge their distorted thoughts and behaviors related to food, weight, and body image.
Family-Based Therapy (FBT)
FBT involves the family in the treatment process, empowering them to support the individual’s recovery.
Medication
Medication may be used to manage symptoms of anxiety, depression, or obsessive-compulsive disorder that may accompany anorexia nervosa.
Recovery and Relapse Prevention

Stages of Recovery
Risk Factors for Relapse
Relapse Prevention Strategies, Lasting improvement for a person with anorexia nervosa depends on
Long-Term Outcomes: Lasting Improvement For A Person With Anorexia Nervosa Depends On
Recovery Rates
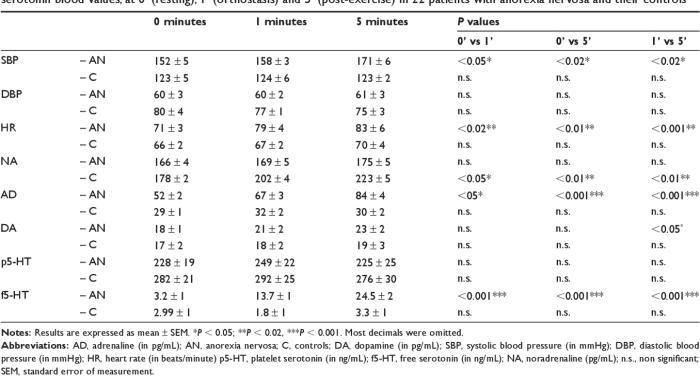
Recovery rates vary, but studies indicate that approximately 50-60% of individuals with anorexia nervosa achieve full recovery.
Physical and Mental Health Complications
Anorexia nervosa can have long-term physical and mental health consequences, including malnutrition, osteoporosis, infertility, and depression.
Factors Influencing Long-Term Outcomes
Helpful Answers
What are the common psychological factors that contribute to anorexia nervosa?
Individuals with anorexia nervosa often exhibit perfectionism, low self-esteem, and a distorted body image.
How does family and social support influence recovery from anorexia nervosa?
A supportive family and social network can provide emotional encouragement, challenge negative thoughts, and assist with practical aspects of recovery.
What are the key components of evidence-based therapies for anorexia nervosa?
Cognitive-behavioral therapy and family-based therapy are effective treatments that focus on changing maladaptive thoughts and behaviors.
What are the potential long-term health complications of anorexia nervosa?
Anorexia nervosa can lead to malnutrition, osteoporosis, heart problems, and other serious health issues.