Chapter 22 descent with modification a darwinian view of life – Chapter 22: Descent with Modification – Darwin’s Enduring Legacy presents a comprehensive exploration of Darwin’s groundbreaking theory of evolution by natural selection. Through compelling narratives and evidence-based analysis, this chapter delves into the fundamental principles that have shaped our understanding of the diversity of life on Earth.
Darwin’s theory revolutionized the scientific landscape, providing a framework for understanding the intricate relationships between species and the processes that drive their adaptation and diversification. This chapter examines the core concepts of variation, inheritance, and selection, illustrating how these mechanisms have played a pivotal role in shaping the evolution of life.
Darwin’s Theory of Natural Selection
Charles Darwin’s theory of natural selection, proposed in his groundbreaking work “On the Origin of Species” in 1859, is a fundamental principle of evolutionary biology. It explains how populations of organisms change over time through a process of differential survival and reproduction.
The theory is based on three key principles:
Variation
Individuals within a population exhibit variation in their traits. This variation can be due to genetic mutations, environmental factors, or a combination of both.
Inheritance
Traits are inherited from parents to offspring. This means that individuals who inherit favorable traits are more likely to pass them on to their offspring.
Selection
Individuals with favorable traits are more likely to survive and reproduce in a given environment. This means that these individuals will contribute more offspring to the next generation, and their favorable traits will become more common in the population over time.
Descent with Modification: Chapter 22 Descent With Modification A Darwinian View Of Life
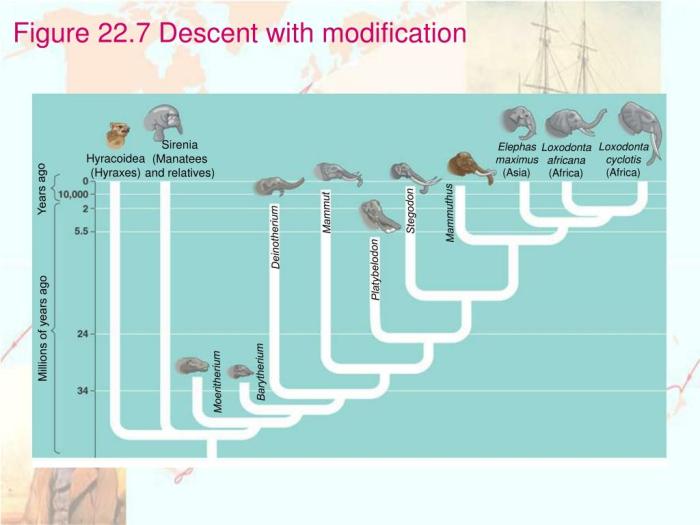
Descent with modification is the idea that all living organisms share a common ancestor and have evolved over time from that ancestor. This concept was first proposed by Darwin and has been supported by a vast amount of evidence from various fields of biology.
Fossil Record
The fossil record provides a historical record of the evolution of life on Earth. Fossils show that organisms have changed over time, and that new species have arisen from ancestral forms.
Comparative Anatomy, Chapter 22 descent with modification a darwinian view of life
Comparative anatomy compares the anatomical structures of different organisms. This can reveal homologous structures, which are structures that share a common evolutionary origin, providing evidence for descent with modification.
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology studies the genetic material of organisms. By comparing DNA sequences, scientists can determine the evolutionary relationships between different species and trace their ancestry back to a common ancestor.
Evidence for Evolution

There is overwhelming evidence to support the theory of evolution, including evidence from the fossil record, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, and biogeography.
Fossil Record
The fossil record provides a historical record of the evolution of life on Earth. Fossils show that organisms have changed over time, and that new species have arisen from ancestral forms.
Comparative Anatomy, Chapter 22 descent with modification a darwinian view of life
Comparative anatomy compares the anatomical structures of different organisms. This can reveal homologous structures, which are structures that share a common evolutionary origin, providing evidence for evolution.
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology studies the genetic material of organisms. By comparing DNA sequences, scientists can determine the evolutionary relationships between different species and trace their ancestry back to a common ancestor.
Biogeography
Biogeography studies the distribution of organisms on Earth. This can provide evidence for evolution by showing how species have adapted to different environments and how their distribution has changed over time.
Evolution of Humans

Humans are a relatively young species, having evolved from a common ancestor with chimpanzees approximately 6 million years ago. The fossil record, comparative anatomy, and molecular biology all provide evidence to support the theory of human evolution.
Fossil Record
The fossil record provides evidence for the evolution of humans from ape-like ancestors. Fossils show that humans have evolved from bipedal ancestors that walked upright and had smaller brains. Over time, human brains have enlarged, and our bodies have become more adapted to walking upright.
Comparative Anatomy, Chapter 22 descent with modification a darwinian view of life
Comparative anatomy reveals that humans share many anatomical similarities with chimpanzees, our closest living relatives. These similarities include the structure of our bones, muscles, and organs, providing evidence for our common ancestry.
Molecular Biology
Molecular biology provides strong evidence for the evolution of humans from chimpanzees. By comparing DNA sequences, scientists have found that humans and chimpanzees share over 98% of their DNA, providing strong evidence for our close evolutionary relationship.
Applications of Evolutionary Theory

Evolutionary theory has a wide range of practical applications in fields such as medicine, agriculture, and conservation biology.
Medicine
Evolutionary theory can be used to understand the evolution of diseases and to develop new treatments. For example, understanding the evolution of antibiotic resistance has helped scientists develop new antibiotics to combat infections.
Agriculture
Evolutionary theory can be used to improve crop yields and livestock production. For example, understanding the evolution of resistance to pests and diseases has helped farmers develop more resistant crops and livestock.
Conservation Biology
Evolutionary theory can be used to inform conservation efforts. For example, understanding the evolutionary history of endangered species can help conservationists develop strategies to protect them and their habitats.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of descent with modification in Darwin’s theory?
Descent with modification refers to the concept that all living organisms share a common ancestor and have undergone gradual changes over time. This concept is central to Darwin’s theory of evolution, as it explains the diversity of life on Earth and the relationships between different species.
How does natural selection contribute to descent with modification?
Natural selection is the driving force behind descent with modification. It favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a particular environment. Over time, these advantageous traits become more common in the population, leading to gradual changes and the evolution of new species.
What evidence supports the theory of descent with modification?
There is a vast body of evidence supporting the theory of descent with modification, including the fossil record, comparative anatomy, molecular biology, and biogeography. These lines of evidence provide compelling insights into the evolutionary history of different species and the interconnectedness of all living organisms.