Cognitive therapists believe that generalized anxiety disorder is induced by – Cognitive therapists believe that generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is induced by negative thoughts and cognitive distortions, a perspective that has gained significant traction in understanding the development and maintenance of this condition. This article delves into the core tenets of this belief, exploring the role of triggers, maintaining factors, and the efficacy of cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) in addressing GAD.
Cognitive Therapists’ Perspective on GAD Induction
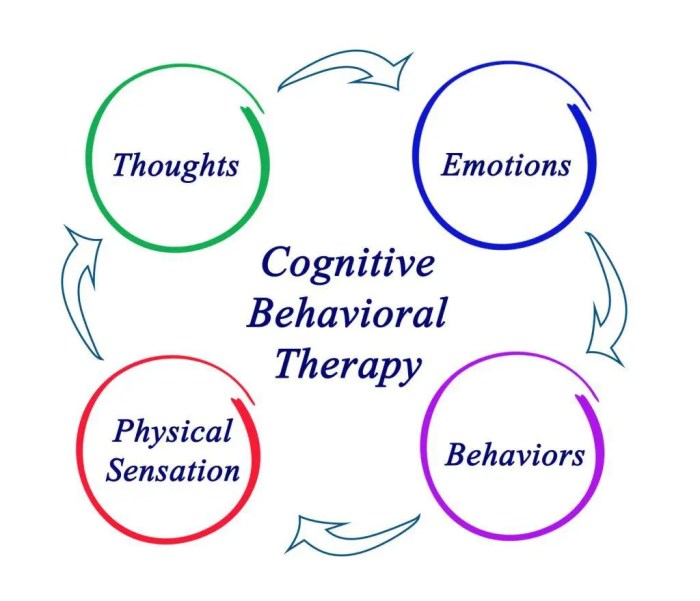
Cognitive therapists believe that generalized anxiety disorder (GAD) is induced by negative thoughts and cognitive distortions. These therapists contend that individuals with GAD tend to hold core beliefs that the world is dangerous and that they are inadequate or vulnerable.
These beliefs lead to negative thoughts and interpretations of situations, which in turn trigger and maintain anxiety.
Triggers and Maintaining Factors, Cognitive therapists believe that generalized anxiety disorder is induced by
Common triggers for GAD include stressful life events, such as job loss or relationship problems, as well as specific situations, such as public speaking or social interactions. Negative thought patterns, such as catastrophizing (exaggerating the severity of a situation) or overgeneralization (assuming that a negative event will occur in all similar situations), contribute to the persistence of GAD by reinforcing the individual’s core beliefs and triggering further anxiety.
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) for GAD
CBT is a widely used treatment approach for GAD that aims to challenge and modify negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to anxiety. CBT therapists work with individuals to identify and challenge their negative thoughts and beliefs, and to develop more adaptive and realistic ways of thinking.
Techniques and Strategies
Specific CBT techniques used to address GAD include:
- Cognitive restructuring: Identifying and challenging negative thoughts and replacing them with more positive and realistic ones.
- Exposure therapy: Gradually exposing individuals to anxiety-provoking situations in a safe and controlled environment to help them develop coping skills and reduce avoidance behaviors.
- Relaxation training: Teaching individuals relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, to manage stress and anxiety.
Research and Evidence
Research findings support the effectiveness of CBT in treating GAD. Studies have shown that CBT can significantly reduce anxiety symptoms and improve overall functioning. However, it is important to note that CBT is not a cure for GAD and may not be effective for everyone.
Alternative Perspectives
Cognitive therapists’ belief about GAD induction is not universally accepted. Some alternative theories or perspectives on the causes of GAD include biological factors, such as genetic predisposition or neurochemical imbalances, and environmental factors, such as early life experiences or trauma.
Frequently Asked Questions: Cognitive Therapists Believe That Generalized Anxiety Disorder Is Induced By
What are the common triggers for GAD?
Stressful life events, specific situations, and negative thought patterns can trigger GAD.
How does CBT help in treating GAD?
CBT challenges and modifies negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to anxiety, promoting healthier coping mechanisms.
Are there any limitations to CBT for GAD?
While CBT is generally effective, its success can vary depending on individual factors, and it may not be suitable for everyone.