Phylogenetic trees pogil answer key – Embark on a captivating journey into the realm of phylogenetic trees with the POGIL answer key, your indispensable guide to deciphering the intricate tapestry of life’s evolutionary history. Delve into the fundamentals of tree construction, interpretation, and applications, unraveling the secrets of our shared ancestry and the diversity of life on Earth.
Phylogenetic Tree Terminology: Phylogenetic Trees Pogil Answer Key
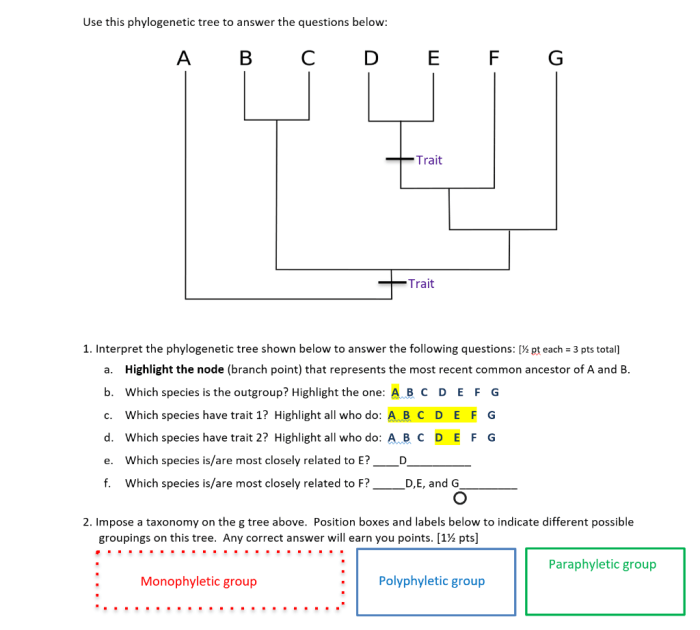
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that represents the evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa. It is a branching diagram that shows the inferred evolutionary history of a group of organisms, based on their shared characteristics.
Root:The root of a phylogenetic tree is the common ancestor of all the taxa in the tree. It is typically represented by a single node at the base of the tree.
Node:A node is a point on a phylogenetic tree where two or more branches meet. Each node represents a hypothetical common ancestor of the taxa that are descended from it.
Branch:A branch is a line that connects two nodes on a phylogenetic tree. It represents the evolutionary lineage of the taxa that are descended from the node at the base of the branch.
Taxon:A taxon is a group of organisms that are classified together based on their shared characteristics. Taxa can be at any level of the taxonomic hierarchy, from species to kingdom.
Rooted and Unrooted Trees:Phylogenetic trees can be either rooted or unrooted. Rooted trees have a designated root node that represents the common ancestor of all the taxa in the tree. Unrooted trees do not have a designated root node, and the root is inferred from the data.
Methods of Constructing Phylogenetic Trees
There are two main methods for constructing phylogenetic trees: distance-based methods and character-based methods.
Distance-Based Methods, Phylogenetic trees pogil answer key
Distance-based methods use a measure of genetic or morphological distance between taxa to construct a tree. Common distance-based methods include:
- Unweighted Pair-Group Method with Arithmetic Mean (UPGMA)
- Neighbor-Joining (NJ)
Character-Based Methods
Character-based methods use a set of characters (e.g., DNA sequences, morphological traits) to construct a tree. Common character-based methods include:
- Parsimony
- Maximum likelihood
Interpreting Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees can be used to infer the evolutionary relationships among different species or other taxa. To read a phylogenetic tree, follow these steps:
- Identify the root of the tree.
- Trace the branches of the tree to find the common ancestors of different taxa.
- Note the length of the branches. Branch length can indicate the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that branch.
- Look for bootstrap values at the nodes of the tree. Bootstrap values indicate the support for each branch.
Applications of Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees are used in a variety of fields, including:
- Evolutionary biology:Phylogenetic trees are used to study the evolution of different species and to infer the history of life on Earth.
- Taxonomy:Phylogenetic trees are used to classify organisms and to determine their relationships to each other.
- Comparative genomics:Phylogenetic trees are used to compare the genomes of different species and to identify conserved genes and regions.
- Inferring ancestral traits:Phylogenetic trees can be used to infer the traits of ancestral species by looking at the traits of their descendants.
Limitations of Phylogenetic Trees
Phylogenetic trees are a powerful tool for studying evolutionary relationships, but they have some limitations. Potential sources of error in phylogenetic tree construction include:
- Incomplete data:Phylogenetic trees are often constructed using incomplete data, which can lead to errors.
- Long-branch attraction:Long-branch attraction is a phenomenon that can lead to incorrect tree topologies when there are long branches in the tree.
- Different methods of tree construction:Different methods of tree construction can lead to different results, which can make it difficult to determine the true evolutionary relationships among different taxa.
Common Queries
What is a phylogenetic tree?
A phylogenetic tree is a diagram that depicts the evolutionary relationships among different groups of organisms, based on their shared ancestry and genetic similarities.
How are phylogenetic trees constructed?
Phylogenetic trees can be constructed using various methods, including distance-based methods (e.g., UPGMA, NJ) and character-based methods (e.g., parsimony, maximum likelihood).
How do I read a phylogenetic tree?
To read a phylogenetic tree, start at the root and follow the branches to the tips. The length of each branch represents the amount of evolutionary change that has occurred along that branch.