An observer in a lighthouse 350 feet above the sea faces unique challenges and experiences that shape their daily life and perspectives. From the solitude and isolation of their remote post to the awe-inspiring views and technological advancements that connect them to the outside world, these observers play a vital role in maritime safety and contribute to our understanding of the natural world.
Their vantage point offers a unique window into the power and beauty of the ocean, as well as the fragility of human life in the face of nature’s forces. The observer’s role extends beyond mere observation, as they also serve as guardians of the sea, reporting unusual phenomena and emergencies, and providing a beacon of hope to those who navigate the treacherous waters below.
Environmental Impacts on an Observer in a Lighthouse 350 Feet
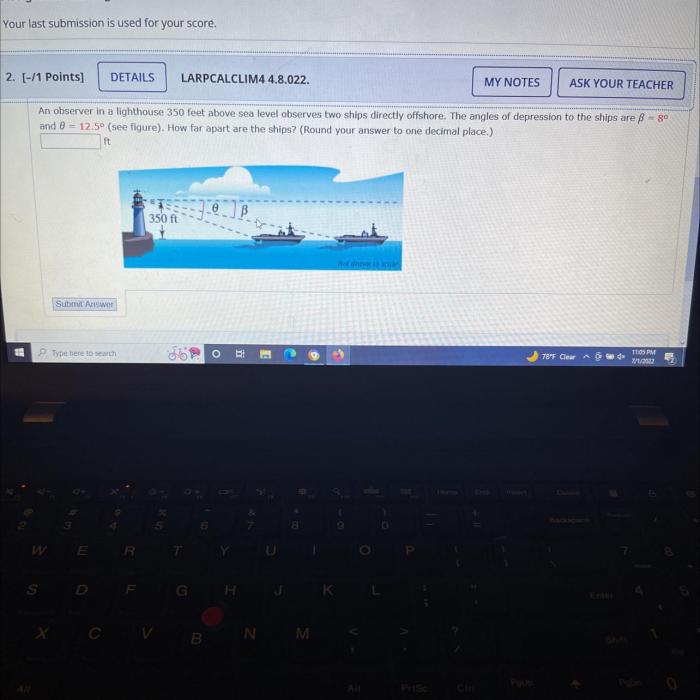
Observers stationed in lighthouses 350 feet above sea level face unique environmental challenges that significantly impact their well-being.
Extreme Weather Conditions
The extreme height of the lighthouse exposes the observer to intense winds, heavy precipitation, and fluctuating temperatures. These conditions can cause physical discomfort, fatigue, and even injuries. The observer must adapt to the constant rocking and swaying of the lighthouse, which can be disorienting and nauseating.
Isolation and Solitude
The isolation and solitude of being stationed in a lighthouse can have profound psychological effects. The observer may experience loneliness, boredom, and a sense of disconnection from the outside world. Prolonged isolation can lead to anxiety, depression, and other mental health issues.
Physical and Mental Health Impacts
The combined effects of extreme weather conditions and isolation can take a toll on the observer’s physical and mental health. They may experience sleep disturbances, muscle tension, headaches, and gastrointestinal problems. The psychological challenges of isolation can also manifest as irritability, mood swings, and difficulty concentrating.
The Role of Technology in an Observer’s Daily Life

Equipment and Tools for Monitoring and Recording Data
Observers in lighthouses rely on specialized equipment and tools to monitor and record weather conditions, sea conditions, and other relevant data. This equipment includes anemometers, barometers, hygrometers, and telescopes. The observer uses these tools to collect accurate and reliable data that is essential for forecasting and safety.
Communication and Connectivity
Technology plays a vital role in keeping the observer connected with the outside world. Radios, satellite phones, and internet access allow the observer to communicate with colleagues, family, and emergency services. This connectivity provides a sense of security and reduces the psychological impact of isolation.
Safety Measures
Technology also enhances the safety of the observer. Automated systems monitor the lighthouse’s structural integrity, detect potential hazards, and trigger alarms in case of emergencies. These systems help ensure the well-being of the observer and the safe operation of the lighthouse.
Unique Observations and Experiences of an Observer
Celestial Events and Weather Patterns
From their vantage point high above sea level, observers in lighthouses have a unique perspective on celestial events and weather patterns. They can observe stars, planets, and constellations with exceptional clarity. They also witness firsthand the formation and movement of clouds, storms, and other atmospheric phenomena.
Tracking Unusual Phenomena and Emergencies
Observers in lighthouses play a crucial role in tracking unusual phenomena and reporting emergencies. They are often the first to spot ships in distress, fires, or other incidents that require assistance. Their observations and reports help ensure the safety of mariners and coastal communities.
Anecdotes and Stories
Observers in lighthouses often have fascinating stories to share about their experiences. They may encounter wildlife, witness historical events, or simply observe the changing seasons from their unique vantage point. These stories provide a glimpse into the lives of these dedicated individuals and the challenges and rewards they face.
The Historical and Cultural Significance of Lighthouses
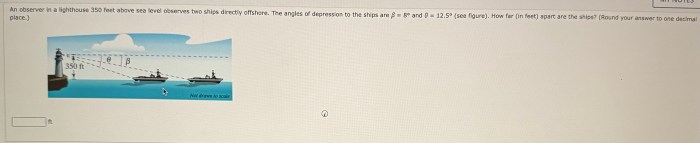
A Brief History of Lighthouses
Lighthouses have a long and rich history, dating back to ancient times. The earliest lighthouses were simple towers or beacons that burned wood or oil to produce light. Over time, lighthouses evolved to become more sophisticated, with the use of lenses, mirrors, and automated systems.
Cultural Significance
Lighthouses have become iconic symbols of hope, safety, and maritime heritage. They represent the connection between land and sea, and have played a vital role in the development of seafaring and trade.
Famous Lighthouses, An observer in a lighthouse 350 feet
There are many famous and notable lighthouses around the world. Some examples include the Alexandria Lighthouse in Egypt, the Eddystone Lighthouse in England, and the Cape Hatteras Lighthouse in the United States. These lighthouses have become landmarks and tourist attractions, and continue to serve as symbols of the importance of maritime safety.
FAQ Section: An Observer In A Lighthouse 350 Feet
What are the primary responsibilities of an observer in a lighthouse?
Observers in lighthouses are responsible for monitoring and recording weather and sea conditions, maintaining the lighthouse and its equipment, and reporting any unusual phenomena or emergencies.
How do observers in lighthouses cope with the isolation and solitude of their work?
Observers in lighthouses often develop coping mechanisms such as keeping a journal, reading, or pursuing hobbies to maintain their mental well-being during extended periods of isolation.
What technological advancements have improved the lives of observers in lighthouses?
Technological advancements such as automated weather stations, remote monitoring systems, and satellite communications have greatly improved the safety and efficiency of lighthouse observers, allowing them to stay connected with the outside world and receive assistance in case of emergencies.