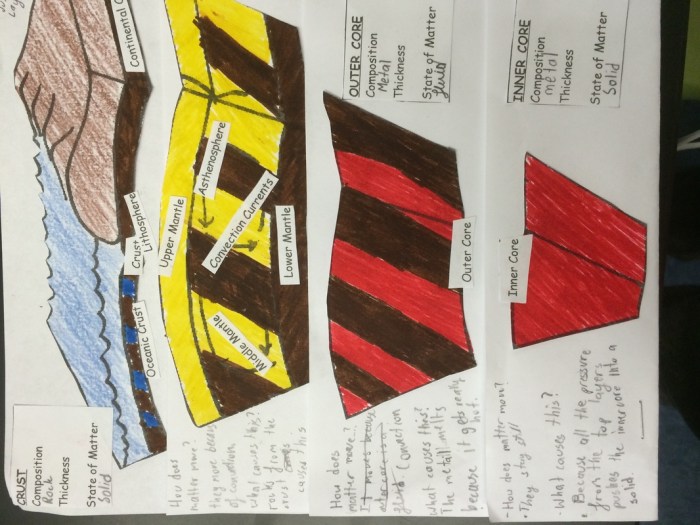
The earth layers foldable answer key – Delving into the Earth’s layers foldable answer key, we embark on a journey to unravel the intricate composition and characteristics of our planet. This comprehensive guide unveils the secrets of each layer, providing a solid foundation for understanding the Earth’s structure and dynamics.
As we traverse through the Earth’s mantle, outer core, and inner core, we uncover the unique properties that define each stratum. From the role of the crust in plate tectonics to the significance of convection currents in the mantle, this foldable answer key offers a panoramic view of the Earth’s inner workings.
Earth’s Layers Overview
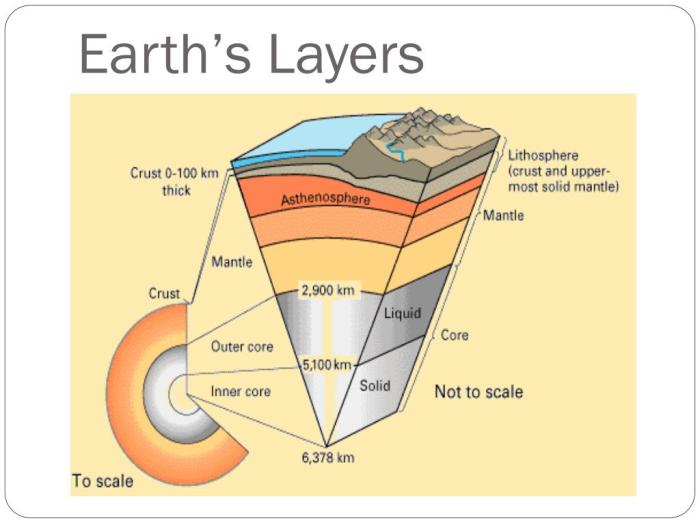
The Earth is a dynamic planet with a complex internal structure. It is composed of several layers, each with distinct characteristics and properties. Understanding the Earth’s layers is crucial for studying its composition, geological processes, and the forces that shape our planet.
Earth’s Layers Visualization
The following table provides a visual representation of the Earth’s layers, their approximate thicknesses, and densities:
| Layer | Thickness (km) | Density (g/cm3) |
|---|---|---|
| Crust | 0-70 | 2.7-3.0 |
| Mantle | 2,900 | 3.4-4.4 |
| Outer Core | 2,200 | 9.9-12.2 |
| Inner Core | 1,220 | 12.8-13.1 |
Crust
The crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is relatively thin compared to the other layers. It is composed primarily of silicate minerals and varies in thickness from 0 km under the oceans to about 70 km under the continents.
The crust is divided into two main types: oceanic crust and continental crust.
- Oceanic crustis denser and thinner than continental crust and is found beneath the oceans. It is composed mainly of basalt and gabbro.
- Continental crustis less dense and thicker than oceanic crust and is found beneath the continents. It is composed mainly of granite and andesite.
The crust plays a crucial role in plate tectonics, the process that drives the movement of the Earth’s lithosphere.
Mantle
The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, extending from the base of the crust to a depth of about 2,900 km. It is composed primarily of silicate minerals and is divided into two main layers: the upper mantle and the lower mantle.
- Upper mantleis less dense and more viscous than the lower mantle and is the site of convection currents that drive plate tectonics.
- Lower mantleis denser and more rigid than the upper mantle and is thought to be largely solid.
The mantle is responsible for the Earth’s heat transfer and plays a crucial role in the generation of the Earth’s magnetic field.
Outer Core
The outer core is a liquid layer that extends from a depth of about 2,900 km to about 5,100 km. It is composed primarily of iron and nickel and is the source of the Earth’s magnetic field.
The outer core is thought to be in a state of rapid rotation, which generates electric currents that create the Earth’s magnetic field. This magnetic field protects the Earth from harmful solar radiation and is essential for life on our planet.
Inner Core, The earth layers foldable answer key
The inner core is a solid layer that extends from a depth of about 5,100 km to the center of the Earth. It is composed primarily of iron and is the densest layer of the Earth.
The inner core is thought to be in a solid state due to the immense pressure at its depth. It is responsible for stabilizing the Earth’s rotation and plays a crucial role in maintaining the Earth’s magnetic field.
Commonly Asked Questions: The Earth Layers Foldable Answer Key
What is the significance of the Earth’s crust?
The crust plays a crucial role in plate tectonics, influencing the movement of tectonic plates and the formation of mountains, volcanoes, and earthquakes.
How does the mantle contribute to the Earth’s dynamics?
The mantle’s convection currents drive the movement of tectonic plates, shaping the Earth’s surface features and influencing volcanic and seismic activity.
What is the unique characteristic of the Earth’s inner core?
The inner core is solid due to the immense pressure and temperature at its depth, contributing to the Earth’s magnetic field and stabilizing its rotation.