Balance each equation by inserting coefficients as needed – Balancing chemical equations by inserting coefficients is a fundamental skill in chemistry. It ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, satisfying the law of conservation of mass. This process plays a crucial role in stoichiometry, thermodynamics, and various other chemical calculations.
Understanding how to balance equations is essential for accurate predictions and interpretations in chemical reactions. This guide will provide a comprehensive overview of the methods and techniques involved in balancing chemical equations, empowering learners with the knowledge to tackle complex reactions with confidence.
1. Overview of Balancing Chemical Equations
Chemical equations are symbolic representations of chemical reactions. They show the reactants, products, and the stoichiometry of the reaction. Balancing chemical equations is essential to ensure that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation.
This ensures that the law of conservation of mass is upheld, which states that mass can neither be created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction.
Balancing chemical equations is also important for quantitative analysis. By balancing equations, we can determine the exact amounts of reactants and products involved in a reaction. This information is essential for predicting the yield of a reaction and for designing chemical processes.
2. Methods for Balancing Equations
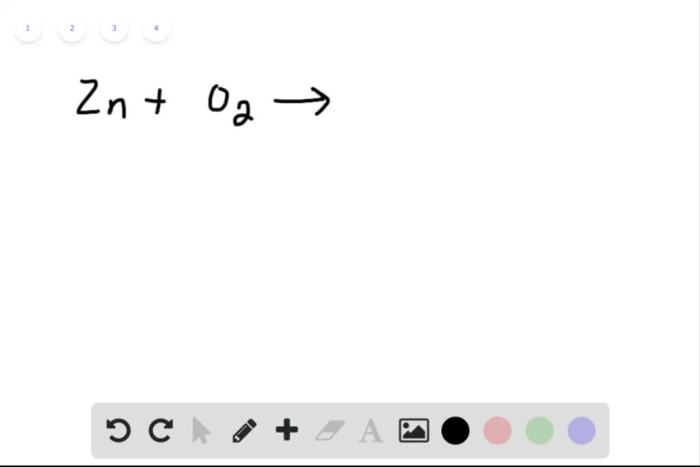
Step-by-Step Guide to Balancing Equations
- Write the unbalanced equation.
- Identify the atoms that are not balanced.
- Add coefficients to the reactants and products to balance the atoms one at a time.
- Check the equation to make sure that all atoms are balanced.
Coefficients
Coefficients are numbers that are placed in front of chemical formulas to indicate the number of molecules or atoms of that substance that are involved in the reaction. For example, in the equation 2H 2+ O 2→ 2H 2O, the coefficient 2 in front of H 2indicates that two molecules of hydrogen are involved in the reaction.
Balancing Simple Equations, Balance each equation by inserting coefficients as needed
Simple equations can be balanced by trial and error. Start by balancing the atoms that appear in the smallest number of molecules. Once those atoms are balanced, move on to the atoms that appear in the next smallest number of molecules, and so on.
Balancing Complex Equations
Complex equations can be balanced using a variety of methods. One common method is the half-reaction method. This method involves breaking the equation down into two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction. The half-reactions are then balanced separately, and the two half-reactions are combined to form the balanced equation.
3. Examples of Balanced Equations
| Equation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 2H2 + O2 → 2H2O | This is a simple redox reaction. Hydrogen is oxidized from a neutral state to a +1 oxidation state, while oxygen is reduced from a neutral state to a
|
| NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O | This is a simple acid-base reaction. NaOH is a strong base, and HCl is a strong acid. The products are NaCl, a salt, and H2O, water. |
| CaCO3→ CaO + CO 2 | This is a simple decomposition reaction. CaCO3, calcium carbonate, decomposes into CaO, calcium oxide, and CO 2, carbon dioxide. |
4. Troubleshooting Common Mistakes

There are a number of common mistakes that students make when balancing chemical equations.
Some of the most common mistakes include:
- Not balancing all of the atoms.
- Using fractional coefficients.
- Changing the subscripts of the reactants or products.
To avoid these mistakes, it is important to follow the step-by-step guide to balancing equations carefully. It is also helpful to practice balancing equations regularly.
5. Advanced Balancing Techniques: Balance Each Equation By Inserting Coefficients As Needed
Half-Reactions
Half-reactions are used to balance redox reactions. A redox reaction is a reaction in which one substance is oxidized and another substance is reduced. Oxidation is the loss of electrons, while reduction is the gain of electrons.
To balance a redox reaction using the half-reaction method, the following steps are taken:
- The reaction is divided into two half-reactions, one for oxidation and one for reduction.
- The half-reactions are balanced separately.
- The two half-reactions are combined to form the balanced equation.
Balancing Redox Equations Using the Half-Reaction Method
To balance a redox equation using the half-reaction method, the following steps are taken:
- Identify the substance that is being oxidized and the substance that is being reduced.
- Write the half-reaction for the oxidation process.
- Write the half-reaction for the reduction process.
- Balance the atoms in each half-reaction.
- Balance the charges in each half-reaction.
- Multiply the half-reactions by appropriate factors so that the number of electrons lost is equal to the number of electrons gained.
- Add the two half-reactions together to form the balanced equation.
6. Applications of Balanced Equations

Balanced chemical equations are used in a variety of fields, including chemistry, engineering, and environmental science.
- In chemistry, balanced equations are used to calculate the stoichiometry of reactions. This information is essential for predicting the yield of a reaction and for designing chemical processes.
- In engineering, balanced equations are used to design chemical reactors and to predict the performance of chemical processes.
- In environmental science, balanced equations are used to model the fate of pollutants in the environment.
Balanced equations are an essential tool for understanding and predicting the behavior of chemical reactions. They are used in a wide variety of fields, and they play a vital role in our understanding of the world around us.
Answers to Common Questions
What is the purpose of balancing chemical equations?
Balancing chemical equations ensures that the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides of the equation, satisfying the law of conservation of mass.
How do I balance simple chemical equations?
To balance simple equations, adjust the coefficients in front of each chemical formula until the number of atoms of each element is the same on both sides.
What are some common mistakes when balancing equations?
Common mistakes include changing the subscripts of chemical formulas, adding or removing atoms, and neglecting to balance all elements.