Which of the following statements is true of glial cells? This intriguing inquiry invites us on an intellectual journey into the fascinating realm of these enigmatic cells, unveiling their pivotal role in supporting and maintaining the intricate tapestry of the nervous system.
Glial cells, often overshadowed by their neuronal counterparts, play a symphony of vital functions, from providing structural support and nourishment to neurons to orchestrating intricate neurochemical exchanges and orchestrating immune defense mechanisms. Their multifaceted nature has captivated scientists, leading to groundbreaking discoveries that illuminate their profound influence on neurological health and disease.
1. Characteristics of Glial Cells
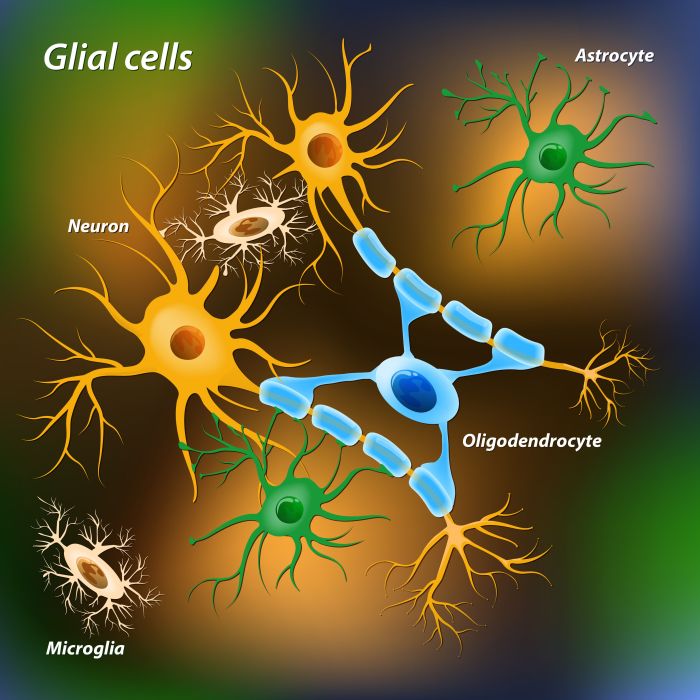
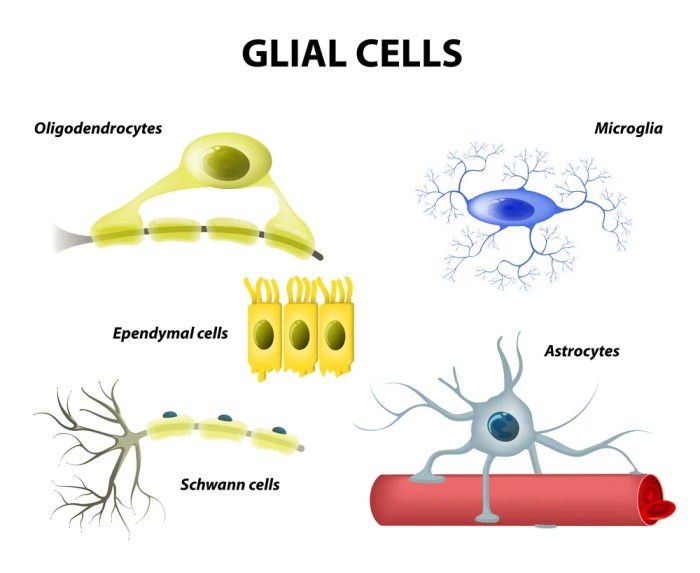
Glial cells, often referred to as neuroglia, are a diverse group of non-neuronal cells that play crucial roles in supporting and maintaining the nervous system. Unlike neurons, glial cells do not generate or transmit electrical impulses. Instead, they perform a wide range of functions essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system.Glial
cells are characterized by their unique morphology, which includes a variety of shapes and sizes. They are typically smaller than neurons and have fewer and shorter processes. Glial cells also exhibit a high degree of plasticity, allowing them to adapt to changes in the environment and respond to injury.
Questions Often Asked: Which Of The Following Statements Is True Of Glial Cells
What distinguishes glial cells from neurons?
Unlike neurons, glial cells lack the ability to generate and transmit electrical impulses. Instead, they exhibit a unique repertoire of functions that support and maintain neuronal activity.
How do glial cells contribute to synaptic plasticity?
Glial cells actively participate in synaptic remodeling by releasing signaling molecules that influence the formation, strengthening, and elimination of synapses, shaping the dynamic nature of neural circuits.
What is the role of glial cells in neurodegenerative diseases?
Dysfunction of glial cells has been implicated in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. Understanding these alterations could lead to novel therapeutic strategies.